
All Global Pandemics: A Historical Overview
The history of humanity is punctuated by numerous pandemics, each leaving its unique mark on societies worldwide. Here, we explore all notable global pandemics that have shaped human history, examining their origins, geographic spread, total deaths, and broader impacts.
GLOBAL ISSUESEDUCATION/KNOWLEDGEBIOGRAPHY/HISTORYENVIRONMENT
Sachin K Chaurasiya
5/12/20242 min read


1889–1890 Pandemic (Russian Flu)
Disease: Influenza (H2N2 virus)
Total Deaths: Approximately 1 million
Impact: The first true global influenza pandemic highlighted the role of global transportation in disease spread.
Year: 1889–1890
Italian Plague
Disease: Bubonic Plague
Total Deaths: About 1 million
Impact: Devastated Northern Italian economies; decreased population significantly.
Year: 1629–1631
Cholera Pandemic
Disease: Cholera
Total Deaths: Over 1 million
Impact: Influenced major public health reforms and sanitation measures.
Year: 1846–1860
Naples Plague
Disease: Bubonic Plague
Total Deaths: Around 1.25 million
Impact: Led to severe depopulation and economic decline in Naples.
Year: 1656–1658
Persian Plague
Disease: Bubonic Plague
Total Deaths: Approximately 2 million
Impact: major demographic changes in Persian territories.
Year: 1772–1773
Japanese Smallpox Epidemic
Disease: Smallpox
Total Deaths: 1 million
Impact: Significant population decrease; affected the Japanese nobility heavily.
Year: 735–373
Cocoliztli Epidemic of 1576
Disease: Hemorrhagic fever
Total Deaths: 2 to 2.5 million
Impact: One of the largest epidemics in the New World; vast depopulation of the indigenous population.
Year: 1576
Hong Kong Flu
Disease: Influenza (H3N2 virus)
Total Deaths: About 1 million
Impact: Spurred global pandemic planning and vaccine development.
Year: 1968-1969
Influenza Pandemic (Asian Flu)
Disease: Influenza (H2N2 virus)
Total Deaths: 1-2 million
Impact: Prompted improvements in pandemic response strategies worldwide.
Year: 1957–1958
Russia Typhus Epidemic
Disease: Typhus
Total Deaths: 2–3 million
Impact: Compounded the chaos and devastation of the post-World War I period in Russia.
Year: 1918–1922
Mexico Smallpox Epidemic
Disease: Smallpox
Total Deaths: Unestimated but significant
Impact: Played a crucial role in the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire.
Year: 1520
Antonine Plague
Disease: Likely smallpox or measles
Total Deaths: 5 million
Impact: It weakened the Roman military and economic structure considerably.
Year: 165–180 AD
Cocoliztli Epidemic of 1545–1548
Disease: Likely hemorrhagic fever
Total Deaths: Millions (exact numbers unclear)
Impact: Resulted in a catastrophic population decline of the indigenous peoples in Mexico
Year: 1545-1548
Third Plague Pandemic
Disease: Bubonic Plague
Total Deaths: Over 12 million (mostly in India and China)
Impact: Spurred the development of public health systems and sanitary reforms
Year: 1855-1960
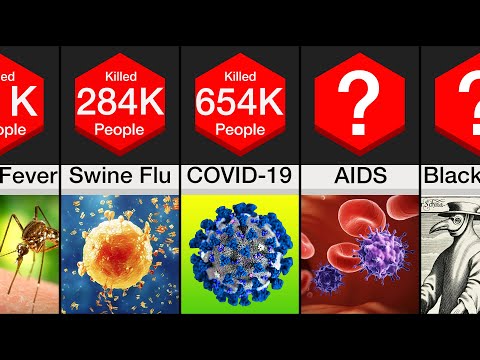
COVID-19 Pandemic
Disease: Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)
Total Deaths: Over 6.9 million reported by early 2023
Impact: Massive global social and economic disruption; accelerated vaccine research
Year: 2019-Present
Black Death
Disease: Bubonic Plague
Total Deaths: Estimated 75–200 million
Impact: One of the deadliest pandemics in human history, leading to massive population declines, social upheaval, and long-lasting economic consequences across Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Year: 1346–1353
HIV/AIDS Pandemic
Disease: HIV/AIDS
Total Deaths: Over 32 million
Impact: Identified in 1981, the HIV/AIDS pandemic has had a devastating global impact, leading to widespread loss of life, social stigma, and significant public health challenges. It remains an ongoing major public health issue worldwide.
Year: 1981-Present
Plague of Justinian
Disease: Bubonic Plague
Total Deaths: Estimated 25-50 million
Impact: One of the first major recorded pandemics, it severely impacted the Byzantine Empire and surrounding territories, contributing to the decline of Byzantine power.
Year: 541–549
Spanish Flu Pandemic
Disease: Influenza (H1N1 virus)
Total Deaths: Estimated 50 million
Impact: This exceptionally deadly influenza pandemic was one of the worst disease outbreaks in recorded history, with a massive global death toll that exceeded even the casualties of World War I.
Year: 1918–1920
These historical pandemics showcase the devastating impact infectious diseases can have on human populations, economies, and societies. The lessons learned from these outbreaks have shaped modern public health practices and pandemic preparedness efforts, though the ongoing threat of emerging and re-emerging diseases remains a significant challenge.
Subscribe to our newsletter
All © Copyright reserved by Accessible-Learning
| Terms & Conditions
Knowledge is power. Learn with Us. 📚


